|
Hey there, We bring you a very cool open source project from a 404 Media reader today that is dedicated to showing how pervasive automated license plate readers have become not just in the United States, but the entire world. If you know of any projects that have a similar vibe to this, please let me know! Side note: It seems like the decentralized Twitter alternative Bluesky got a ton of new users over the weekend. If you're on there, here's a link to follow our accounts. -Jason On his drive to move from Washington state to Huntsville, Alabama, Will Freeman began noticing lots of cameras. “So I moved to Alabama, and on my way there, once I started getting into the South, I saw a ton of these black poles with a creepy looking camera and a solar panel on top,” Freeman told me. “I took a picture of it and ran it through Google, and it brought me to the Flock website. And then I knew like, ‘Oh, that’s a license plate reader.’ I started seeing them all over the place and realized that they were for the police. And I didn’t like that.” Flock is one of the largest vendors of automated license plate readers (ALPRs) in the country. The company markets itself as having the goal to fully “eliminate crime” with the use of ALPRs and other connected surveillance cameras, a target experts say is impossible.
This segment is a paid ad. If you’re interested in advertising, let's talk.

Generative AI (GenAI) chatbots are changing the way businesses engage with customers by providing intelligent, round-the-clock support. However, this technology comes with serious risks, including the potential for unsafe responses and the mishandling of sensitive requests, which can jeopardize a company’s reputation and customer safety.
In ActiveFence’s latest report, we explore these vulnerabilities via a case study from the travel industry to highlight broader implications for business using GenAI-powered applications. It also examines the challenges faced by travel companies, including risks to brand integrity and safety concerns related to user recommendations. Plus, we provide practical strategies for improving safety measures and protecting your GenAI applications from potential threats.
You’ll also find real-life examples of how our researchers manipulated the AI systems with risky prompts to reveal unsafe advice.
Stay informed and safeguard your business—download the full report today.
In Huntsville, Freeman noticed that license plate reader cameras were positioned in a circle at major intersections, forming a perimeter that could track any car going into or out of the city’s downtown. He started to look for cameras all over Huntsville and the surrounding areas, and soon found that Flock was not the only game in town. He found cameras owned by Motorola, and a third, owned by a company called Avigilon (a subsidiary of Motorola). Flock and automated license plate reader cameras owned by other companies are now in thousands of neighborhoods around the country. Many of these systems talk to each other and plug into other surveillance systems, making it possible to track people all over the country. “It went from me seeing 10 license plate readers to probably seeing 50 or 60 in a few days of driving around,” Freeman said. “I wanted to make a record of these things. I thought, ‘Can I make a database of these license plate readers?’” And so he made a map, and called it DeFlock. DeFlock runs on Open Street Map, an open source, editable mapping software. He began posting signs for DeFlock to the posts holding up Huntsville’s ALPR cameras, and made a post about the project to the Huntsville subreddit, which got good attention from people who lived there. People have been plotting not just Flock ALPRs, but all sorts of ALPRs, all over the world.  The printable sign Freeman encourages people to put on ALPRs “I’ve become good at spotting them just because I’m kind of subconsciously always looking for them,” he said. “I want everyone to be aware that this is happening. And I don’t think I can change people’s minds—some people will be fine with it. But some people won’t be,” he said. “And hopefully enough people won’t be fine with it and will do something to get them taken down [in their city] or at least better controlled, preferably taken down.” When I first talked to Freeman, DeFlock had a few dozen cameras mapped in Huntsville and a handful mapped in Southern California and in the Seattle suburbs. A week later, as I write this, DeFlock has crowdsourced the locations of thousands of cameras in dozens of cities across the United States and the world. “It still just scratches the surface,” Freeman said. “I added another page to the site that tracks cities and counties who have transparency reports on Flock’s site, and many of those don’t have any reported ALPRs though, so it’ll help people focus on where to look for them.” He said so far more than 1,700 cameras have been reported in the United States and more than 5,600 have been reported around the world. He has also begun scraping parts of Flock’s website to give people a better idea of where to look to map them. For example, Flock says that Colton, California, a city with just over 50,000 people outside of San Bernardino, has 677 cameras. 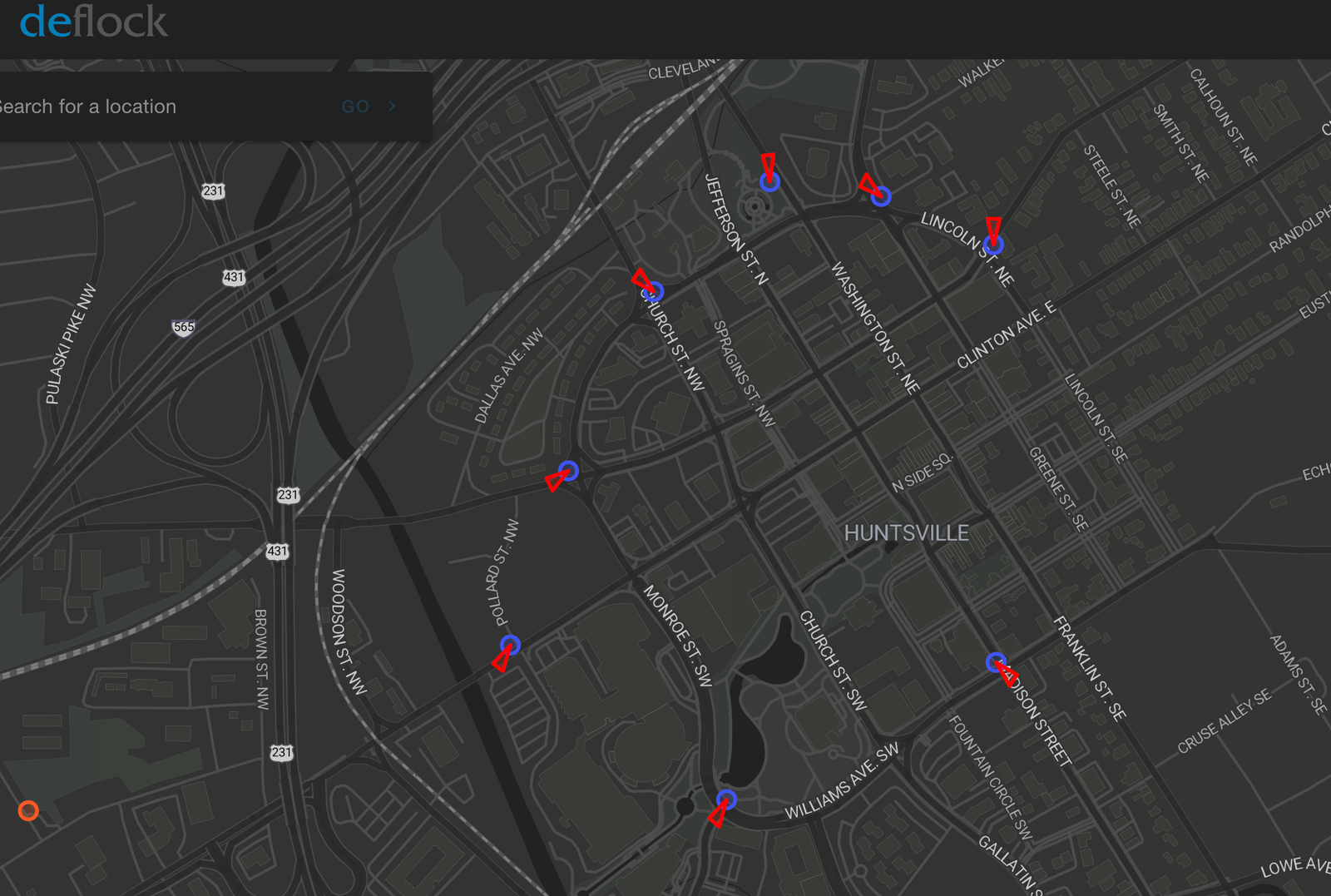 A ring of Flock cameras in Huntsville's downtown, pointing outward. People who submit cameras to DeFlock have the ability to note the direction that they are pointing in, which can help people understand how these cameras are being positioned and the strategies that companies and police departments are using when deploying them. For example, all of the cameras in downtown Huntsville are pointing away from the downtown core, meaning they are primarily focused on detecting cars that are entering downtown Huntsville from other areas. Freeman also said he eventually wants to find a way to offer navigation directions that will allow people to avoid known ALPR cameras. The fact that it is impossible to drive in some cities without being passing ALPR cameras that track and catalog your car’s movements is one of the core arguments in a Fourth Amendment challenge to Flock’s existence in Norfolk, Virginia; this project will likely show how infeasible traveling without being tracked actually is in America. Knowing where they are is the first step toward resisting them.
|